Himanshu Kaushik | TNN | Updated: Aug 18, 2019, 12:47 IST
A
bigger cause of concern is that only 20% of this livestock is hunted
while about 50% is scavenged feed, which includes either dying or dead
animals abandoned by locals, especially gaushalas, home to old,
unproductive and ill cattle.
The study, ‘Ecology of Lion in agro-pastoral Gir landscape, Gujarat’, has been conducted by a team of Wildlife Institute of India (WII) researchers Y V Jhala, Kausik Banerjee and Parabita Basu It needs mention that Sarasiya Virdi in Amreli district — the epicenter of the deadly Canine Distemper Virus outbreak that killed 29 lions last year — was one such dumping ground of ill and dead cattle.
The forest department doesn’t allow disposal of carcasses in the area.
According to the study, a high percentage of killing of livestock by lions in villages outside the protected area augurs intense man-animal conflict in the future.
Last counted in 2015, Gujarat housed 523 lions. The number is estimated to have swelled to over 700.
Of these, about 50% live outside the protected area mainly in four neighbouring districts namely Bhavnagar, Amreli, Porbandar and Gir Somnath. Lion experts, however, flag a more serious concern.
Easy prey blunting hunting skills of Asiatic lions, say foresters
As lions move out of the wild and get closer to humans, easy availability of livestock, especially baits and dead animals, is blunting hunting skills of lions, especially cubs,” said Wildlife Institute of India (WII) researchers Y V Jhala.He recounts how they witnessed a cub feeding on a live bait in revenue area without first killing it.
Forest officials suggested disposal of cattle carcasses in lion habitats should not be allowed.
“This will ensure lions are mandated to kill livestock or wild ungulates in the area and keep their hunting skills honed,” he said.“This would also prevent outbreak of CDV like diseases as sick and dead cattle are eaten by dogs which are carriers of deadly CDV virus,” the official added.
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/ahmedabad/gujarat-predator-lions-turn-scavengers-outside-gir/articleshow/70720294.cms
Highlights
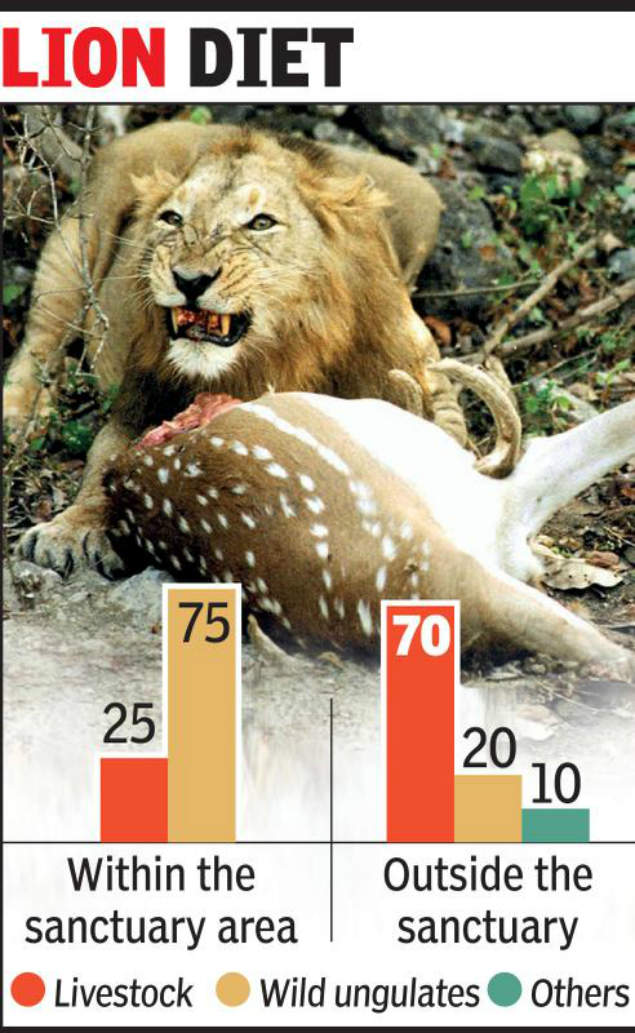
- A study on feeding habits of lions in Gujarat reveals that 75% of lion food inside the Gir sanctuary is hunted wildlife.
- However, outside the sanctuary 70% of their food consists of livestock.
- According
to the study, a high percentage of killing of livestock by lions in
villages outside the protected area augurs intense man-animal conflict
in the future.
A path-breaking study on feeding habits of lions in Gujarat reveals that 75% of lion food inside the Gir sanct...Read MoreAHMEDABAD: As it moves away from the wild, closer to humans, the king of the jungle is hunting less and scavenging more.A path-breaking study on feeding habits of lions in Gujarat reveals that 75% of lion food inside the Gir sanctuary is hunted wildlife. However, outside the sanctuary 70% of their food consists of livestock.
The study, ‘Ecology of Lion in agro-pastoral Gir landscape, Gujarat’, has been conducted by a team of Wildlife Institute of India (WII) researchers Y V Jhala, Kausik Banerjee and Parabita Basu It needs mention that Sarasiya Virdi in Amreli district — the epicenter of the deadly Canine Distemper Virus outbreak that killed 29 lions last year — was one such dumping ground of ill and dead cattle.
The forest department doesn’t allow disposal of carcasses in the area.
According to the study, a high percentage of killing of livestock by lions in villages outside the protected area augurs intense man-animal conflict in the future.
Last counted in 2015, Gujarat housed 523 lions. The number is estimated to have swelled to over 700.
Of these, about 50% live outside the protected area mainly in four neighbouring districts namely Bhavnagar, Amreli, Porbandar and Gir Somnath. Lion experts, however, flag a more serious concern.
Easy prey blunting hunting skills of Asiatic lions, say foresters
As lions move out of the wild and get closer to humans, easy availability of livestock, especially baits and dead animals, is blunting hunting skills of lions, especially cubs,” said Wildlife Institute of India (WII) researchers Y V Jhala.He recounts how they witnessed a cub feeding on a live bait in revenue area without first killing it.
Top Comment
It’s their territory.. We humans r encroaching the Jungle.
Mayank Detroja
See All CommentsAdd comment
Forest officials suggested disposal of cattle carcasses in lion habitats should not be allowed.
“This will ensure lions are mandated to kill livestock or wild ungulates in the area and keep their hunting skills honed,” he said.“This would also prevent outbreak of CDV like diseases as sick and dead cattle are eaten by dogs which are carriers of deadly CDV virus,” the official added.
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/ahmedabad/gujarat-predator-lions-turn-scavengers-outside-gir/articleshow/70720294.cms
No comments:
Post a Comment